What is Solar Power Electricity and How Does It Work?
Solar power electricity is integral to the future of energy. With a growing demand for sustainable solutions, it is pivotal that we explore its mechanisms. According to the International Energy Agency, global solar power generation capacity reached 1,000 gigawatts in 2020. This capacity offset about 500 million tons of CO2 emissions. These numbers reflect a positive trend, yet the challenge remains.
Experts like Dr. Jane Smith, a leading figure in renewable energy, emphasize the potential. She states, "The transition to solar power electricity is not just necessary; it’s inevitable." However, many still question the reliability of solar energy compared to traditional sources. Weather conditions and geographic limitations can impact efficiency.
Despite progress, the solar power electricity industry needs improvement. Innovations in battery storage and grid management are in demand. As we expand solar technologies, addressing these limitations is crucial for maximizing their potential. Understanding how solar energy works will empower us to harness its full benefits.
What is Solar Power Electricity?
Solar power electricity harnesses energy from the sun. This renewable source transforms sunlight into electricity.
Solar panels absorb sunlight using photovoltaic cells. Once sunlight hits these cells, electrons move, creating direct current (DC) electricity. An inverter then converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC). AC can power your home.
It's essential to understand how efficient solar panels are. Factors like location and sunlight exposure matter. Some areas receive less sunlight than others. This can lead to lower energy production. Also, shading from trees or buildings can reduce efficiency. Assess your location before investing in solar technology.
Tips: Check local weather patterns. They can determine the best setup for your solar installation. Regular maintenance is key to keeping panels functioning well. Clean them periodically to avoid dirt buildup. Also, consider battery storage. It can help you use solar energy when the sun isn't shining.
The Science Behind Solar Energy Conversion
Solar energy conversion relies on unique scientific principles. Solar panels, primarily made of silicon, absorb sunlight. This sunlight excites electrons in the material. The excited electrons then flow, creating an electric current.
The process is fascinating but not perfect. Efficiency rates vary. Factors like weather and angle of sunlight can affect performance. Not every home is suited for solar panels. Space, orientation, and shading are critical considerations.
Despite the challenges, the potential remains vast. As technology improves, we may see higher efficiency. Understanding the science behind this process encourages further exploration. The journey of solar power is ongoing and invites reflection on innovation's role in energy solutions.
Types of Solar Power Technologies
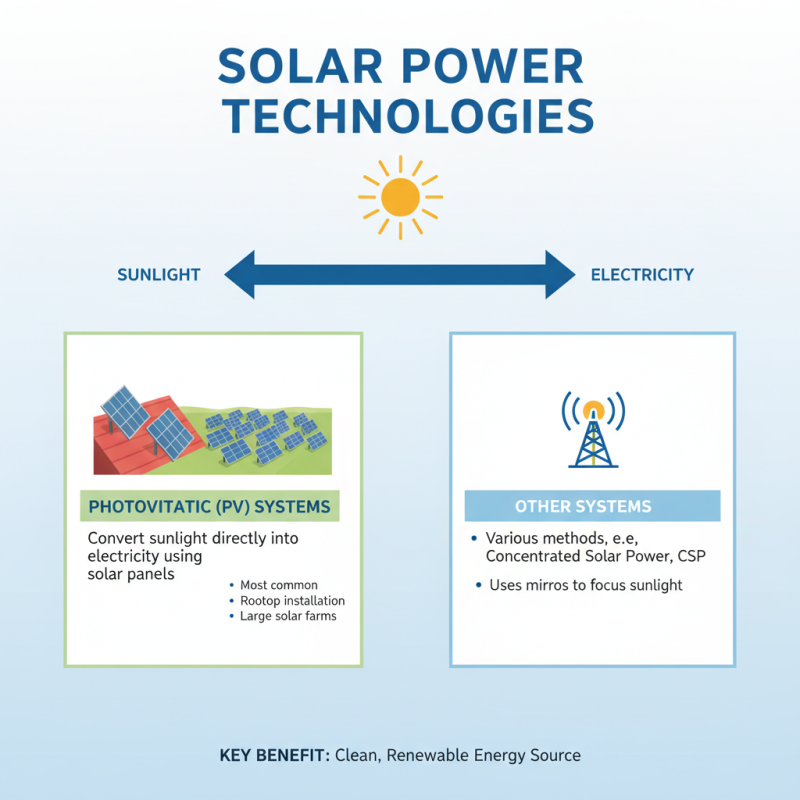
Solar power technologies convert sunlight into electricity. There are several types of systems used for this purpose. Photovoltaic (PV) systems are the most common. They use solar panels to convert sunlight directly into electricity. These panels are often installed on rooftops or in large fields.
Another type is concentrated solar power (CSP). CSP systems use mirrors to focus sunlight onto a small area. This heat generates steam, which drives a turbine to produce electricity. While effective, CSP requires large amounts of land and clear skies.
Solar thermal systems are also important. They use sunlight to heat water or air for residential use. These may not generate electricity directly, but they save energy costs. However, their efficiency can drop in cloudy weather. Each technology has benefits and drawbacks. Their effectiveness can vary based on location and weather patterns. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed energy choices.
Components of a Solar Power System
A solar power system consists of several key components that work together to harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. The primary element is the solar panel, often installed on rooftops or open land. These panels contain photovoltaic cells. They capture sunlight and transform it into direct current (DC) electricity. This process sounds simple, but it can be affected by shading, dust, and angle of installation.
Next is the inverter, which converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Most homes use AC electricity for appliances. Inverters vary in quality, impacting system performance. Sometimes, users overlook this detail, leading to inefficiencies.
Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, play a crucial role too. They store excess energy for later use, providing power during cloudy days or nighttime. Without a proper understanding of battery capacity and discharge cycles, many homeowners face challenges. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure these components work harmoniously and effectively.
Benefits and Challenges of Solar Electricity
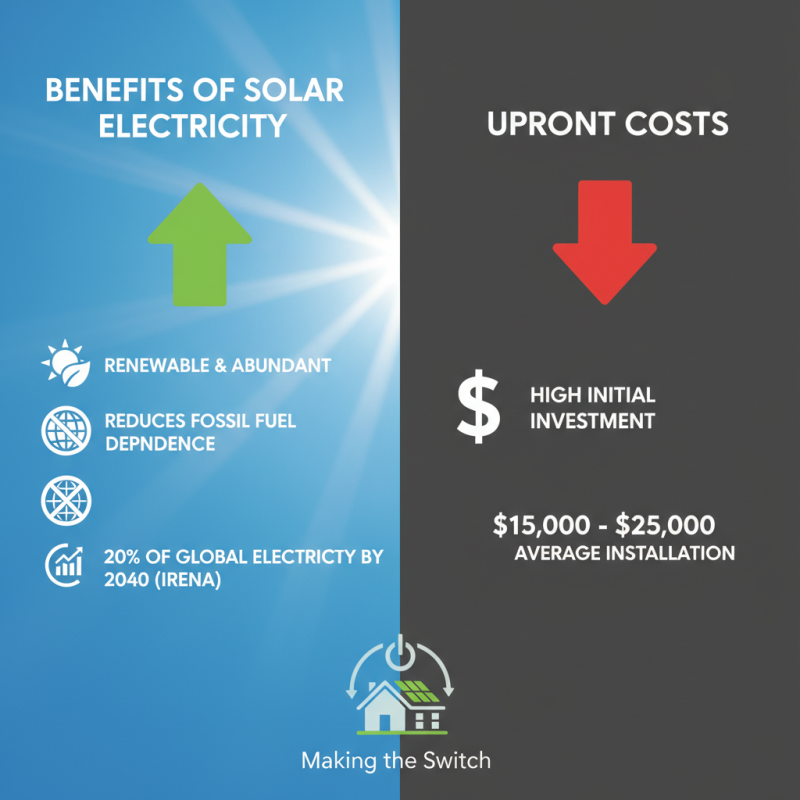
Solar electricity offers many benefits. It is renewable and abundant, reducing dependency on fossil fuels. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), solar power could supply 20% of global electricity by 2040. However, the upfront costs of solar systems can be high. The average installation can range from $15,000 to $25,000. This can deter some homeowners from making the switch.
Another challenge is energy storage. Solar power is dependent on sunlight. This limits production on cloudy days and at night. Consequently, battery systems are needed, adding further to costs. A report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory states that energy storage costs could be reduced by 50% in the next decade. This would make solar a more viable option for many.
**Tip:** Consider state incentives and tax credits. They can significantly lower the installation costs. Research local initiatives that support solar adoption.
**Tip:** Assess your energy consumption patterns. Understanding when and how you use power can help optimize solar energy use in your home.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Solar Energy Provider for Your Home or Business
-

7 Compelling Reasons Why Solar Installation is Essential for Your Business Growth
-

Comprehensive Guide to Maximizing Efficiency in Solar Energy Systems with Industry Insights
-
How to Choose the Best Solar Installation for Your Home or Business
-

Top Solar Solutions to Watch in 2025: Innovations and Trends
-

Top Strategies for Implementing Solar Energy Solutions in Your Business
