What is a solar power system and how does it work?
Solar power systems are gaining significant traction as a sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources. Leading expert Dr. Emily Thompson emphasizes, "Harnessing the sun's energy is our best chance for a cleaner future." This reflects the growing recognition of solar power systems in addressing energy needs and environmental concerns.
Understanding how these systems work is crucial. A solar power system typically includes solar panels, an inverter, and a battery. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. The inverter then transforms this electricity into a usable form for homes and businesses. This process is not without challenges. Energy storage can be inefficient and the initial costs remain high for many consumers.
Moreover, not every location is ideal for solar installations. Weather patterns and geographic factors play a significant role in effectiveness. Although solar power systems present a promising solution, the journey to widespread adoption requires overcoming technical and economic hurdles. As we explore this topic, it's essential to focus on both the potential and the limitations of solar energy.
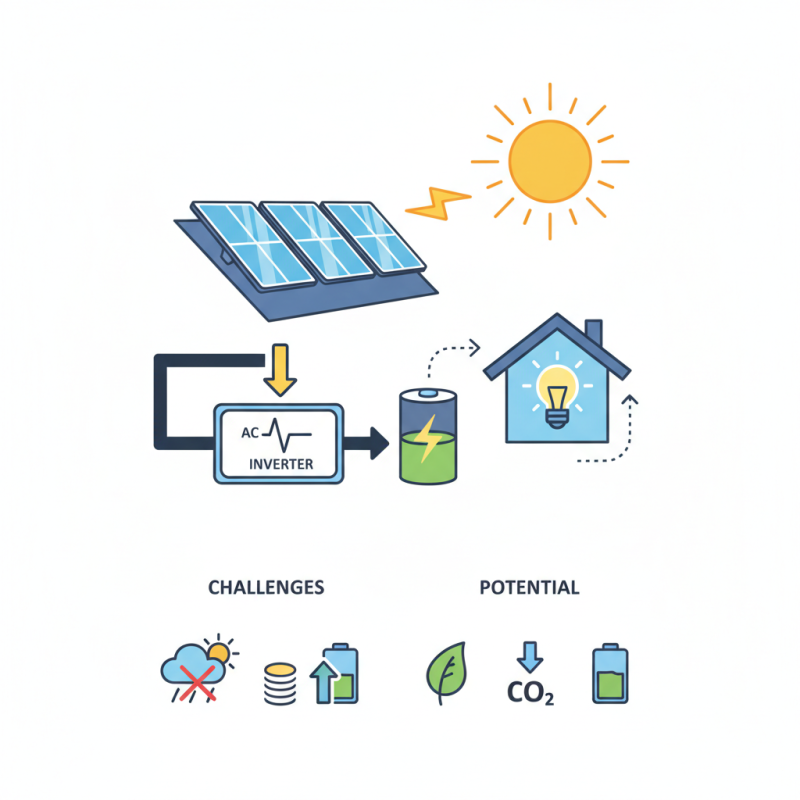
What is a solar power system?
A solar power system converts sunlight into electricity. This technology harnesses solar energy using panels, inverters, and batteries. Typically, solar panels are placed on rooftops. They work by absorbing sunlight and converting it into direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity then passes through an inverter, which changes DC to alternating current (AC) for home use.
Installing solar panels can significantly reduce energy bills. However, not all roofs are suitable for solar. It is crucial to find a location with optimal sunlight exposure. Shade from trees or buildings can lower efficiency. Regular maintenance is needed too. Dust and debris might accumulate on the panels. This buildup reduces their performance.
When considering solar energy, research is key. Evaluate potential savings. Look into local incentives or rebates. These can make the system more affordable. Consulting with professionals helps make informed decisions. They can assess your specific energy needs. Implementing a solar system is often a step towards sustainability, but it's not a perfect solution for everyone.
Components of a solar power system
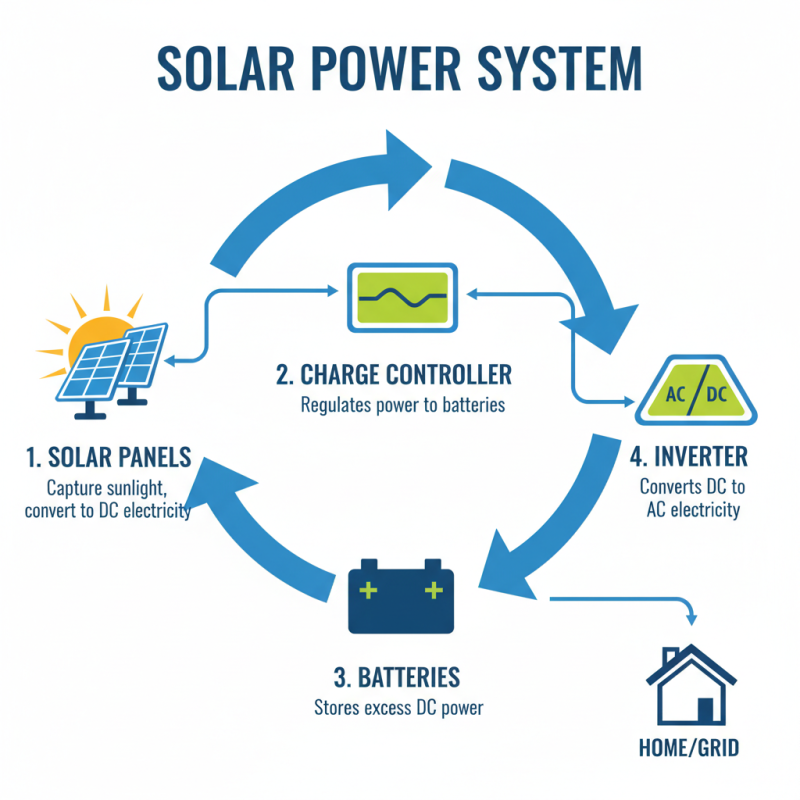
A solar power system converts sunlight into electricity. The main components include solar panels, an inverter, batteries, and a charge controller. Solar panels capture sunlight and transform it into direct current (DC) electricity. They are often mounted on roofs or in open spaces where they receive maximum sunlight.
The inverter plays a crucial role. It converts the DC electricity from the panels into alternating current (AC) for home use. Without an inverter, the system cannot supply power to most household appliances. Batteries store excess electricity for later use, especially during cloudy days or at night.
The charge controller is another critical component. It manages the flow of electricity to and from the batteries. An effective charge controller prevents overcharging and extends battery life. However, improper installation or failure to monitor these components can lead to inefficiencies. System performance may decrease over time if maintenance is neglected. Understanding these components is essential for maximizing the benefits of solar power.
How solar panels convert sunlight into electricity
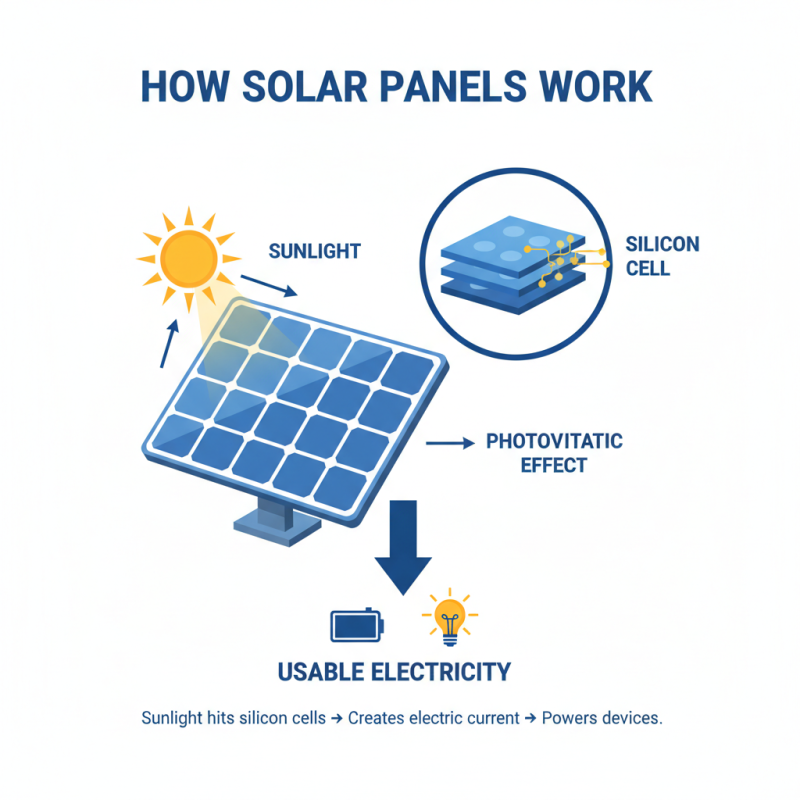
Solar panels are remarkable devices that transform sunlight into usable electricity. They are made up of many smaller units called solar cells. These cells contain materials like silicon, which react to sunlight. When sunlight hits the cells, it creates a flow of electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect.
Each solar panel produces direct current (DC) electricity. However, most homes and businesses use alternating current (AC) electricity. This is where inverters come in. Inverters convert DC into AC. The efficiency of this conversion can vary. Some systems struggle with shading or dirt, which lowers their performance.
Understanding energy needs is crucial. A solar power system can still fall short if it's not sized properly. Poor planning can lead to excess energy during sunny days and shortages during cloudy ones. Regular maintenance is also important. Ignoring small issues can lead to significant drawbacks over time. Balancing these factors ensures an effective solar setup.
The process of electricity generation and distribution
A solar power system converts sunlight into electricity. This process begins with solar panels, which absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity is then transformed into alternating current (AC) by an inverter, making it usable for homes and businesses. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, solar energy accounted for about 3% of total electricity generation in 2022. This figure shows growth potential.
Electricity generated from solar power undergoes distribution through the power grid. Once converted, the electricity travels through transmission lines to reach consumers. Unfortunately, inefficiencies exist in this system. A report from the International Energy Agency indicates that about 10% of electricity can be lost during transmission. This loss counteracts some benefits of renewable energy solutions like solar.
Despite advances, challenges persist in optimizing battery storage for solar energy. Energy stored during peak sunlight hours may not always suffice during high-demand periods. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory notes that energy storage can improve system reliability but remains costly. Such considerations highlight the need for ongoing innovation in solar technology and infrastructure.
Solar Power System: Electricity Generation Process
This chart illustrates the key dimensions related to solar power generation and distribution. Solar radiation is measured in kilowatt-hours per square meter (kWh/m²), showing the amount of sunlight absorbed. Energy conversion efficiency indicates how effectively solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. The chart also shows the total electricity generated in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and distribution losses as a percentage.
Benefits of using solar power systems for energy needs
Solar power systems harness sunlight to generate electricity. They offer significant benefits for energy needs. By converting solar energy into usable power, these systems can lower your electricity bills. According to a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), solar energy can reduce household energy expenses by up to 70%.
Using solar power systems can also have environmental advantages. They produce clean energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory highlights that widespread solar adoption could cut carbon emissions by over 1.5 billion tons annually. This reduction is crucial as climate change continues to pose challenges globally.
However, there are obstacles to consider. Initial installation costs can be high, sometimes reaching $20,000 for a residential system. Not every home has suitable roof space or sunlight exposure. Additionally, battery storage options, while improving, still present challenges in efficiency and cost. These factors can make solar power less accessible for some. Despite these hurdles, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial drawbacks.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Solar Power Systems for Your Home
-

How to Use Solar Electricity to Power Your Home?
-

Top 5 Power Solutions Solar Innovations Reducing Costs and Boosting Efficiency in 2023
-

How to Harness Solar Electricity: Maximize Efficiency with Proven Strategies and Market Insights
-

2025 Top 5 Solar Power Solutions to Revolutionize Your Energy Needs
-

Maximizing Efficiency and Savings with Future Solar Technology
